偏差和方差(bias variance)过拟合 欠拟合(underfit overfit)
泛化能力
如果说一个模型在测试集上表现的与训练集一样好,我们就说这个模型的泛化能力很好;如果模型在训练集上表现良好,但在测试集上表现一般,就说明这个模型的泛化能力不好。
欠拟合与过拟合
训练模型的两个目的:
- 降低训练误差
- 缩小训练误差和测试误差的差距,增强模型的泛化能力
欠拟合:模型在训练集与测试集上表现都不好的而情况。其不能很好的拟合所有的点。
过拟合:训练集上表现良好,测试集上不行。其太认真的拟合所有的点,导致模型的泛化能力很差。(1. dropout 2. regulation 3. bn)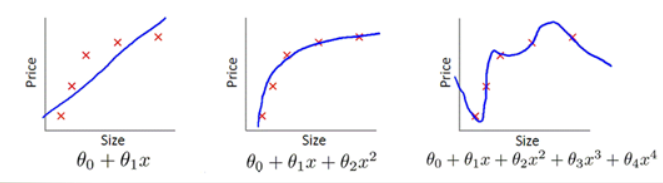
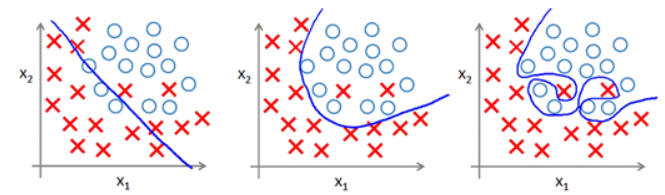
网络的深浅
偏差与方差
误差的两大来源:偏差与方差 $error = bias + variance$
偏差:训练集上的错误率,与训练集成线性关系,模型的精确度
方差:模型在测试集上表现与训练集上的差距,模型的稳定性
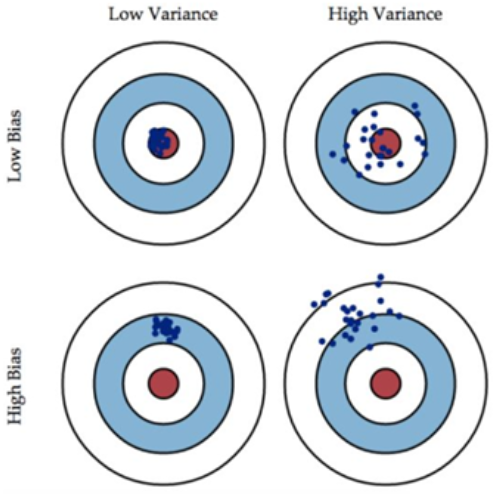
四种情况:
- 偏差很低,方差很高: 意味着训练误差很低,测试误差很高,此时发生了过拟合现象。预测值基本落在真实值周围,但很分散,此时方差较大,说明模型的稳定性不够好。
- 偏差很高,方差很低: 意味着训练误差,测试误差都很高,此时发生了欠拟合现在。预测值与真实值有较大距离,但此时值很集中,方差小;模型的稳定性较好,但预测准确率不高,处于”一如既往地预测不准”的状态。
- 偏差,方差都很高: 是我们最不想看到的结果,此时模型不仅预测不准确,而且还不稳定,每次预测的值都差别比较大。
- 偏差很低,方差很低: 意味着训练误差很低,测试误差也很低,表示我们的模型训练的结果很好。
正则化的目的
防止过拟合的方法:
L1和L2正则化
Lambda因子及其影响
dropout
提前停止(early stopping)
对于过拟合的修正:
- 加入Dropout层
- 检查数据集是否过小(Data Augmentation)
- 用一用迁移学习的思想
- 调参小 tricks:调小学习速率(Learning Rate),调小每次反向传播的训练样本数(batch_size)
- 试一试别的优化器(optimizer)
- Keras 的回调函数 EarlyStopping()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""Untitled13.ipynb
Automatically generated by Colaboratory.
Original file is located at
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1S8gVZuhXjI_JOC_wLxUkCWLDGbZId56w
"""
# import libraries
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchvision import datasets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data.sampler import SubsetRandomSampler
def create_datasets(batch_size):
# percentage of training set to use as validation
valid_size = 0.2
# convert data to torch.FloatTensor
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
# choose the training and test datasets
train_data = datasets.MNIST(root='data',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transform)
test_data = datasets.MNIST(root='data',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=transform)
# obtain training indices that will be used for validation
num_train = len(train_data)
indices = list(range(num_train))
np.random.shuffle(indices)
split = int(np.floor(valid_size * num_train))
train_idx, valid_idx = indices[split:], indices[:split]
# define samplers for obtaining training and validation batches
train_sampler = SubsetRandomSampler(train_idx)
valid_sampler = SubsetRandomSampler(valid_idx)
# load training data in batches
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data,
batch_size=batch_size,
sampler=train_sampler,
num_workers=0)
# load validation data in batches
valid_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data,
batch_size=batch_size,
sampler=valid_sampler,
num_workers=0)
# load test data in batches
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_data,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=0)
return train_loader, test_loader, valid_loader
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28 * 28, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 128)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, x):
# flatten image input
x = x.view(-1, 28 * 28)
# add hidden layer, with relu activation function
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.dropout(x)
# add hidden layer, with relu activation function
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.dropout(x)
# add output layer
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
# initialize the NN
model = Net()
print(model)
# specify loss function
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# specify optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
import numpy as np
import torch
class EarlyStopping:
"""Early stops the training if validation loss doesn't improve after a given patience."""
def __init__(self, patience=7, verbose=False, delta=0):
"""
Args:
patience (int): How long to wait after last time validation loss improved.
Default: 7
verbose (bool): If True, prints a message for each validation loss improvement.
Default: False
delta (float): Minimum change in the monitored quantity to qualify as an improvement.
Default: 0
"""
self.patience = patience
self.verbose = verbose
self.counter = 0
self.best_score = None
self.early_stop = False
self.val_loss_min = np.Inf
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, val_loss, model):
score = -val_loss
if self.best_score is None:
self.best_score = score
self.save_checkpoint(val_loss, model)
elif score < self.best_score + self.delta:
self.counter += 1
print(f'EarlyStopping counter: {self.counter} out of {self.patience}')
if self.counter >= self.patience:
self.early_stop = True
else:
self.best_score = score
self.save_checkpoint(val_loss, model)
self.counter = 0
def save_checkpoint(self, val_loss, model):
'''Saves model when validation loss decrease.'''
if self.verbose:
print(f'Validation loss decreased ({self.val_loss_min:.6f} --> {val_loss:.6f}). Saving model ...')
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'checkpoint.pt')
self.val_loss_min = val_loss
def train_model(model, batch_size, patience, n_epochs):
# to track the training loss as the model trains
train_losses = []
# to track the validation loss as the model trains
valid_losses = []
# to track the average training loss per epoch as the model trains
avg_train_losses = []
# to track the average validation loss per epoch as the model trains
avg_valid_losses = []
# initialize the early_stopping object
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(patience=patience, verbose=True)
for epoch in range(1, n_epochs + 1):
###################
# train the model #
###################
model.train() # prep model for training
for batch, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader, 1):
# clear the gradients of all optimized variables
optimizer.zero_grad()
# forward pass: compute predicted outputs by passing inputs to the model
output = model(data)
# calculate the loss
loss = criterion(output, target)
# backward pass: compute gradient of the loss with respect to model parameters
loss.backward()
# perform a single optimization step (parameter update)
optimizer.step()
# record training loss
train_losses.append(loss.item())
######################
# validate the model #
######################
model.eval() # prep model for evaluation
for data, target in valid_loader:
# forward pass: compute predicted outputs by passing inputs to the model
output = model(data)
# calculate the loss
loss = criterion(output, target)
# record validation loss
valid_losses.append(loss.item())
# print training/validation statistics
# calculate average loss over an epoch
train_loss = np.average(train_losses)
valid_loss = np.average(valid_losses)
avg_train_losses.append(train_loss)
avg_valid_losses.append(valid_loss)
epoch_len = len(str(n_epochs))
print_msg = (f'[{epoch:>{epoch_len}}/{n_epochs:>{epoch_len}}] ' +
f'train_loss: {train_loss:.5f} ' +
f'valid_loss: {valid_loss:.5f}')
print(print_msg)
# clear lists to track next epoch
train_losses = []
valid_losses = []
# early_stopping needs the validation loss to check if it has decresed,
# and if it has, it will make a checkpoint of the current model
early_stopping(valid_loss, model)
if early_stopping.early_stop:
print("Early stopping")
break
# load the last checkpoint with the best model
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('checkpoint.pt'))
return model, avg_train_losses, avg_valid_losses
batch_size = 256
n_epochs = 100
train_loader, test_loader, valid_loader = create_datasets(batch_size)
# early stopping patience; how long to wait after last time validation loss improved.
patience = 20
model, train_loss, valid_loss = train_model(model, batch_size, patience, n_epochs)
请多多指教。
文章标题:偏差和方差(bias variance)过拟合 欠拟合(underfit overfit)
本文作者:顺强
发布时间:2019-02-01, 23:59:00
原始链接:http://shunqiang.ml/cnn-bias-variance/版权声明: "署名-非商用-相同方式共享 4.0" 转载请保留原文链接及作者。

