YOLO9000 Better, Faster, Stronger
YOLO (You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection) V2
对比V1版本的优化: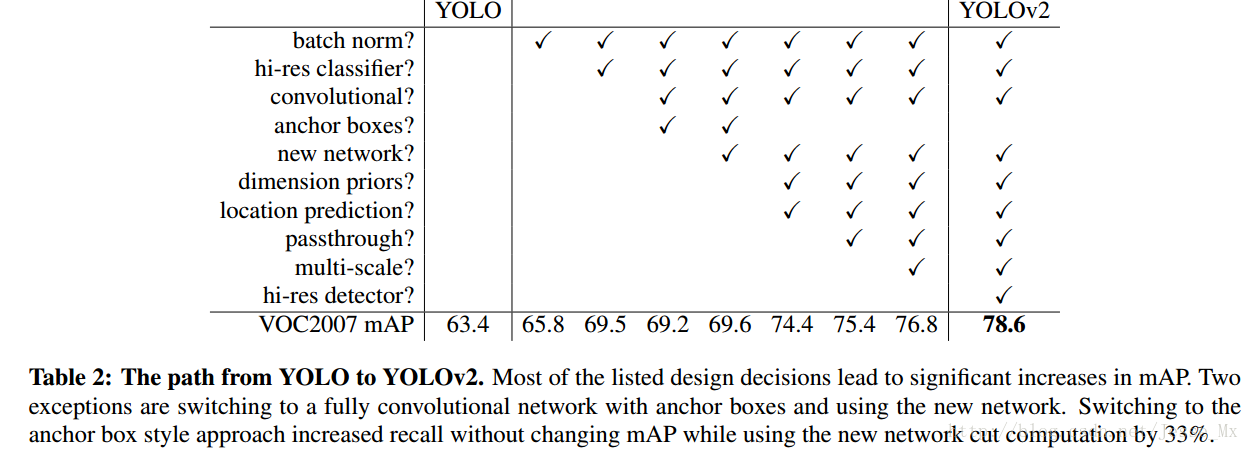
Batch Normalization
CNN在训练过程中网络每层输入的分布一直在改变, 会使训练过程难度加大,但可以通过normalize每层的输入解决这个问题。新的YOLO网络在每一个卷积层后添加batch normalization,通过这一方法,mAP获得了2%的提升。batch normalization 也有助于规范化模型,可以在舍弃dropout优化后依然不会过拟合。
High Resolution Classifier
对于YOLOv2,作者首先对分类网络(自定义的darknet)进行了fine tune,分辨率改成448 * 448,在ImageNet数据集上训练10轮(10 epochs),训练后的网络就可以适应高分辨率的输入了。然后,作者对检测网络部分(也就是后半部分)也进行fine tune。这样通过提升输入的分辨率,mAP获得了4%的提升。
Convolutional With Anchor Boxes
YOLOv2去掉了全连接层,使用anchor boxes预测bounding boxes。
YOLOv2去掉了一个池化层,使得卷积层的输出有更高的分辨率。
YOLOv2将输入图像的尺寸从448 448缩减到416 416,这样特征图的输出就是一个奇数,有一个中心栅格。作者观察到,有很多物体,尤其是较大的物体往往会位于图像的中心。有一个中心栅格的话可以用中心栅格专门去负责预测这些中心落在图像中心附近的物体,而不需要图像中心附近的4个栅格去预测这些物体。YOLOv2对图像进行了32倍的降采样(factor为32),最终输出的特征图尺寸是13 * 13 。
Algorithm
iou计算:
def iou(box1,box2):
xi1 = max(box1[0],box2[0])
yi1 = max(box1[1],box2[1])
xi2 = max(box1[2],box2[2])
yi2 = max(box1[3],box2[3])
inter_area = (xi2-xi1)*(yi2-yi1)
box1_area = (box1[3]-box1[1])*(box1[2]-box1[0])
box2_area = (box2[3]-box2[1])*(box2[2]-box2[0])
union_area = (box1_area + box2_area)-inter_area
iou = inter_area/union_area
return iou
box1=(2,1,3,4)
box2=(1,2,3,4)
print("iou="+str(iou(box1,box2)))
Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)
非极大值抑制算法
- 作用:
以目标检测为例:目标检测的过程中在同一目标的位置上会产生大量的候选框,这些候选框相互之间可能会有重叠,此时我们需要利用非极大值抑制找到最佳的目标边界框,消除冗余的边界框。 算法流程:
根据置信度得分进行排序
选择置信度最高的比边界框添加到最终输出列表中,将其从边界框列表中删除
计算所有边界框的面积
计算置信度最高的边界框与其它候选框的IoU。
删除IoU大于阈值的边界框
重复上述过程,直至边界框列表为空。def nms(bounding_boxes, confidence_score, threshold): """ describe: Non-max Suppression Algorithm :param bounding_boxes: list Object candidate bounding boxes :param confidence_score: list Confidence score of bounding boxes :param threshold: float IoU threshold :return picked_boxes: list Rest boxes after nms operation :return picked_score: list The score of rest boxes after nms operation """ # If no bounding boxes, return empty list if len(bounding_boxes) == 0: return [], [] # Bounding boxes boxes = np.array(bounding_boxes) # coordinates of bounding boxes start_x = boxes[:, 0] start_y = boxes[:, 1] end_x = boxes[:, 2] end_y = boxes[:, 3] # Confidence scores of bounding boxes score = np.array(confidence_score) # Picked bounding boxes picked_boxes = [] picked_score = [] # Compute areas of bounding boxes areas = (end_x - start_x + 1) * (end_y - start_y + 1) # Sort by confidence score of bounding boxes order = np.argsort(score) # Iterate bounding boxes while order.size > 0: # The index of largest confidence score index = order[-1] # Pick the bounding box with largest confidence score picked_boxes.append(bounding_boxes[index]) picked_score.append(confidence_score[index]) # Compute ordinates of intersection-over-union(IOU) x1 = np.maximum(start_x[index], start_x[order[:-1]]) x2 = np.minimum(end_x[index], end_x[order[:-1]]) y1 = np.maximum(start_y[index], start_y[order[:-1]]) y2 = np.minimum(end_y[index], end_y[order[:-1]]) # Compute areas of intersection-over-union w = np.maximum(0.0, x2 - x1 + 1) h = np.maximum(0.0, y2 - y1 + 1) intersection = w * h # Compute the ratio between intersection and union ratio = intersection / (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - intersection) left = np.where(ratio < threshold) order = order[left] return picked_boxes, picked_score
请多多指教。
文章标题:YOLO9000 Better, Faster, Stronger
本文作者:顺强
发布时间:2020-03-18, 23:59:00
原始链接:http://shunqiang.ml/cnn-yolov2/版权声明: "署名-非商用-相同方式共享 4.0" 转载请保留原文链接及作者。

